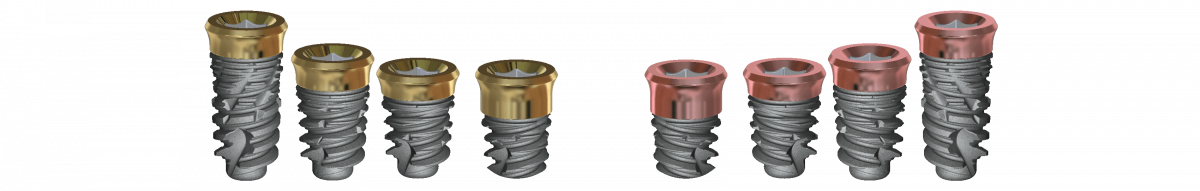
All you need to know about Short implants
Pink Tissue level Vi features a transmucosal collar for one-stage procedures, attaches connective tissue, and creates a biological seal around the implant. The short implant is available in diameters: 4.2, 5.0 with lenses of 8, 6.5, 5, and 4 mm
Novel Coating to minimize Bacterial adhsion.
The coated surfaces significantly reduction of the presence of bacteria, this fact could be important for the health of the peri-implant soft tissues.
Horizontal grooves produced by micro-machining impedes epithelial down growth on titanium implants.
Micro threads provide enhanced initial stability and increases contact area to crestal bone, which will enhance osseointegration at the crestal bone level.
The presence of two spiral channel, self-tapping cutting threads facilitates implant placement and enhance primary stability
Sharp threads and spiral deepening from cervical to apical region, and improved cutting ability, with better bone to implant contact for better primary stability
Grooved threads enhance bone stabilization during primary stabilization and increase the amount of bone to implant contact, enhancing osseointegration.
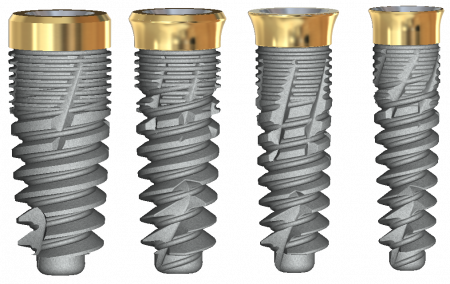
optimized threadform
Anatomically tapered implant body has proprietary reverse buttress threads with wide flat leading edges for increased stability.
Grooved threads enhance bone stabilization during primary stabilization and increase the amount of bone to implant contact, enhancing osseointegration.
Restorative ease
The Pink Tissue Versatile implant offers a conical internal hex connection with 45° central hole.

All you need to know about Short implants
Pink Tissue level Vi features a transmucosal collar for one-stage procedures, attaches connective tissue, and creates a biological seal around the implant. are available in diameters: 4.2, 5.0 and lengths of 8, 6.5, 05, and 04 mm
Novel Coating to minimize Bacterial adhsion.
The coated surfaces significantly reduction of the presence of bacteria, this fact could be important for the health of the peri-implant soft tissues.
Horizontal grooves produced by micro-machining impedes epithelial down growth on titanium implants.
Micro threads provide enhanced initial stability and increases contact area to crestal bone, which will enhance osseointegration at the crestal bone level.
The presence of two spiral channel, self-tapping cutting threads facilitates implant placement and enhance primary stability
Sharp threads and spiral deepening from cervical to apical region, and improved cutting ability, with better bone to implant contact for better primary stability
Grooved threads enhance bone stabilization during primary stabilization and increase the amount of bone to implant contact, enhancing osseointegration.
optimized threadform
Anatomically tapered implant body has proprietary reverse buttress threads with wide flat leading edges for increased stability.
Grooved threads enhance bone stabilization during primary stabilization and increase the amount of bone to implant contact, enhancing osseointegration.
Restorative ease
The Pink Tissue Versatile implant offers a conical internal hex connection with 45° central hole.
Dentalis Gold tissue-level implants offer dentists flexibility in challenging clinical situations. Provided short lengths of 4mm, 5mm, or 6mm, these specialized implants not only allow doctors to safely avoid vital biological structures but also can eliminate the need for many transplant procedures. With the specialized surface offered by Dentalis, longer implants are not necessarily better, and shorter implants can provide a better clinical solution.
Dentalis Gold tissue-level implants offer dentists flexibility in challenging clinical situations. Provided short lengths of 4mm, 5mm, or 6mm, these specialized implants not only allow doctors to safely avoid vital biological structures but also can eliminate the need for many transplant procedures. With the specialized surface offered by Dentalis, longer implants are not necessarily better, and shorter implants can provide a better clinical solution.

The benefits of short implants
Dental implants are the most common and predictable treatment indicated for patients with tooth loss. Although this technique is very effective and successful, there are still instances
of implant failure due to complications such as peri-implantitis.
Peri-implantitis is an inflammatory lesion of the connective tissues around dental implants and is characterized by progressive loss of the supporting bone [1].
Dentalis® offers many products with specific features that have been shown to prevent peri-implantitis, including short implants. As the name implies, short implants are shorter than the standard implant of 8+ mm, usually 7 mm or less, meaning that short implants require less bone for insertion. For patients with severe atrophy (bone loss), short implants offer a viable alternative to complicated, time-consuming, and expensive bone grafting and augmentation procedures. Specifically, regarding maxillary sinus augmentation, an approach that relies on the amount of residual bone present, wherein many complications can occur during or after the surgery—such as tearing of the sinus membrane which increases the chance of infection and healing time, or even injuries to the local nerves—the selection of Dentalis® short implants is clear as a faster, cheaper, and less invasive option. Particularly when a minimal amount of bone is available, less aggressive techniques are available using Dentalis® short implants.
Many studies have shown the efficacy of short implants by evaluateting their success on the basis of marginal bone loss (MBL), survival rate, complications, and prosthesis failure.
The use of short implants has produced results that are on par with those of standard implants for the parameters listed above [2]. Specifically, researchers showed that short implants have the same rate and level of osseointegration, which is the deposition of new bone on the surface of the implant. This process is critical for the survival of the implant [3, 4].
Several studies have shown that most of the stress caused by loading (the force applied when the jaw is closed) is transferred to the cervical portion of the implant, while relatively little force reaches its apical portion, so the length of the implant can be shortened without consequence, as opposed to the diameter which could strongly affect the risk of failure. Researchers have also shown that short implants have high survival rates—with observational studies showing 100% success after 12 month follow-up—and significantly less complications due to their minimally invasive application [5]
The level of marginal bone should be stable for long-term success of the implant.
Short implants have actually been shown to cause less marginal bone loss than longer implants [5, 6].
The thorough scientific evidence has proven short implants to be comparable to long implants, with the added benefits of lower risk of peri-implantitis and bone loss.
Functionally and esthetically, they are an excellent alternative to standard implants in many cases, and their implementation is only growing.
Dentalis® Short implants have been suggested as an easier, less expensive, and quicker alternative to surgical methods for increasing bone volume for the rehabilitation of atrophic edentulous areas.
References:
- Schwarz, F., et al., Peri‐implantitis. Journal of clinical periodontology, 2018. 45: p. S246-S266.
- Karthikeyan, I., S.R. Desai, and R. Singh, Short implants: A systematic review. Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology, 2012. 16(3): p. 302.
- Albrektsson, T. and C. Johansson, Osteoinduction, osteoconduction and osseointegration. European spine journal, 2001. 10(Suppl 2): p. S96-S101.
- Nedir, R., et al., A 7‐year life table analysis from a prospective study on ITI implants with special emphasis on the use of short implants: Results from a private practice. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2004. 15(2): p. 150-157.
- Pardo-Zamora, G., et al., Short dental implants (≤ 8.5 mm) versus standard dental implants (≥ 10 mm): A one-year post-loading prospective observational study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021. 18(11): p. 5683.
- Renouard, F. and D. Nisand, Short implants in the severely resorbed maxilla: a 2‐year retrospective clinical study. Clinical implant dentistry and related research, 2005. 7: p. s104-s110.



The attachment of soft tissue, peri-implant mucosa, surrounding a dental implant creates a seal and is composed of epithelial and connective tissue. The tissue-level design provides for a more stable seal. The coated neck of the implant is antibacterial and prevents the formation of biofilms. State-of-the-art nitriding of titanium allows for increases in the depth of nitrogen diffusion, therefore increasing soft tissue adhesion.
The attachment of soft tissue, peri-implant mucosa, surrounding a dental implant creates a seal and is composed of epithelial and connective tissue. The tissue-level design provides for a more stable seal. The coated neck of the implant is antibacterial and prevents the formation of biofilms. State-of-the-art nitriding of titanium allows for increases in the depth of nitrogen diffusion, therefore increasing soft tissue adhesion.

DESIGNED FOR IMMEDIATE PROTOCOLS
- Fully tapered implant with deep threads and grove threads designed for optimized primary stability combined with the predictability of Tissue Level Implant
- A narrow implant diameter option, 3.25 mm for all indications.

PERI-IMPLANT HEALTH PRESERVATION
- Reduced risk of nesting bacteria
- Novel Coatings to Minimize Bacterial Adhesion, Immediate soft-tissue attachment preservation and Promote Osteoblast Activity for Titanium Implants

REAL CONFIDENCE
- USA precision and quality Titanium Grade 23 material and BAS® surface

- A one-stage process with restoration at soft-tissue level allows you to reduce chair time .
- Ease of restoration even in the posterior region, with the same type of restoration of the Bone level implants
- Highly efficient treatment protocol thanks to straightforward conventional and digitally integrated workflows






Dentalis Surface:
Surface roughness is achieved from “grit-blasting,” using a unique combination of the HA particles (soluble) with different sizes of grains. This process creates optimal structural roughness on the surface and enables the incorporation of biocompatible particles (such as HA and TCP).
The rough surfaces produced by grit-blasting have irregular geometries with a Ra value of 3.3 μm, which is considered optimal for the osseointegration process.
With a Removal torque of 406 Ncm.
References:
Effect of micrometer-scale roughness of the surface of Ti6Al4V pedicle screws in vitro and in vivo.
B.Boyan Published 1 November 2008 Medicine, Materials Science
The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume.
Raw Material:
All Dentalis implants are made of Ti 6Al-4V ELI that is a higher-purity (“extra-low interstitial”) version of Ti 6Al-4V, with lower specified limits on iron and the interstitial elements C and O. It is an alpha + beta alloy .Ti 6Al-4V ELI may be considered in any biomedical application, particularly for implantable components, because of its biocompatibility, good fatigue strength, and low modulus. Ti 6Al-4V ELI has been the material of choice due to its excellent biocompatibility. The ELI grade has superior damage tolerance (fracture toughness, fatigue crack growth rate) and better mechanical properties compared to standard grade Ti 6Al-4V.
Implant Range:
Recommendation
to reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the depth
of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 3.25Ø in soft bone (D4)
use the 2.4 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by Dentalis cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 |

Recommendation
to reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the depth
of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 3.75Ø in soft bone
(D4) use the 2.8 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by Dentalis cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 |

Recommendation
to reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the
depth of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 3.75Ø
in soft bone (D4) use the 2.8 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by Dentalis cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 | 400-600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 | ∅ 4.1 |

Recommendation
to reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the
depth of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 5.0Ø in
soft bone (D4) use the 3.6 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by Dentalis cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 | 400-600 | 300-500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 | ∅ 4.1 | ∅ 4.6 |

- | 4mm | 5mm | 6.5mm | 8mm |
4.2mm | 114204 | 114205 | 114206 | 114208 |
5.0mm | 115004 | 115005 | 115006 |
Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
For over two decades, Dentalis has led implant dentistry into a new era of attainability and aesthetics.
The pink tissue versatile implant neck combines superior
gingival aesthetics and high primary stability,
improved placement, and temporization,
which is particularly beneficial in
aesthetically demanding cases.
REFERENCES:
1.Bittner N, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Gil M. Comparison of Peri-implant Soft Tissue Color with the Use of Pink-Neck vs Gray Implants and Abutments Based on Soft Tissue Thickness:
A 6-Month Follow-up Study. Int J Prosthodont. 2020Jan/Feb;33(1):29-38.
2. Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Bittner N. Comparison of the Color Appearance of Peri-implant Soft Tissue with Natural Gingiva Using Anodized Pink-Neck Implants and Pink Abutments: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019 May/June;34(3):752–758.
3.Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H. A prospective clinical trial to assess the optical efficacy of pink neck implants and pink abutments on soft tissue aesthetics. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017;29(6):1-7.38.
For over two decades, Dentalis has led implant dentistry into a new era of attainability and aesthetics.
The pink tissue versatile implant neck combines superior gingival aesthetics and high primary stability, improved placement, and temporization, which is particularly beneficial in aesthetically demanding cases.

REFERENCES:
1.Bittner N, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Gil M. Comparison of Peri-implant Soft Tissue Color with the Use of Pink-Neck vs Gray Implants and Abutments Based on Soft Tissue Thickness:
A 6-Month Follow-up Study. Int J Prosthodont. 2020Jan/Feb;33(1):29-38.
2. Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Bittner N. Comparison of the Color Appearance of Peri-implant Soft Tissue with Natural Gingiva Using Anodized Pink-Neck Implants and Pink Abutments: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019 May/June;34(3):752–758.
3.Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H. A prospective clinical trial to assess the optical efficacy of pink neck implants and pink abutments on soft tissue aesthetics. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017;29(6):1-7.38.
Dentalis coated tissue level implants provide for a reduction in biofilm accumulations (24%) compared to other uncoated products with significantly higher biofilm accumulation (85%).
Dentalis coatings showed higher anti-bacterial activity and minimized bacterial adhesion without compromising the biocompatibility of the titanium surface. These findings are clinically applicable as the layers can minimize detrimental colonization of P. gingivalis and other pathogens on implant surfaces.
The combination of innovative surface technology with 344% stronger bone reduces marginal bone loss and provides for a higher BIC%, decreasing the risk of peri-implant disease. The enhanced deep thread simplifies the insertion and allows for high primary stability.

