S2 Implant
With its specialized design, it can achieve high primary stability in soft bone, and is primarily recommended for bone types 1 and 2. The S2 design features dual thread and dual spiral channels, shortened drilling protocols, and the capability for self-drilling, self-tapping, and self-condensing bone. With a variety of lengths ranging from 6.5 mm to 18 mm, and diameters ranging from 3mm to 6mm, the S2 can provide clinical solutions in even the most challenging situations.
The S2 implant offers a conical internal hex connection with a 45° central hole.
Superior advantages:

Platform switching enables good adaptation of the gingival tissues to the abutment and prevents cervical bone resorption.

Horizontal grooves produced by micro-machining impedes epithelial down growth on titanium implants.

Micro threads provide enhanced initial stability and increases contact area to crestal bone, which will enhance osseointegration at the crestal bone level.

S2 has Dual thread With his designed S2 provide shorten drilling protocols and self condensing bone .

S2 has Dual spiral channels With his designed S2 provide self driling, self tapping and self condensing bone
Dentalis Surface:
Surface roughness is achieved from “grit-blasting,” using a unique combination of the HA particles (soluble) with different sizes of grains. This process creates optimal structural roughness on the surface the surface, and enables the incorporation of biocompatible particles (such as HA and TCP).
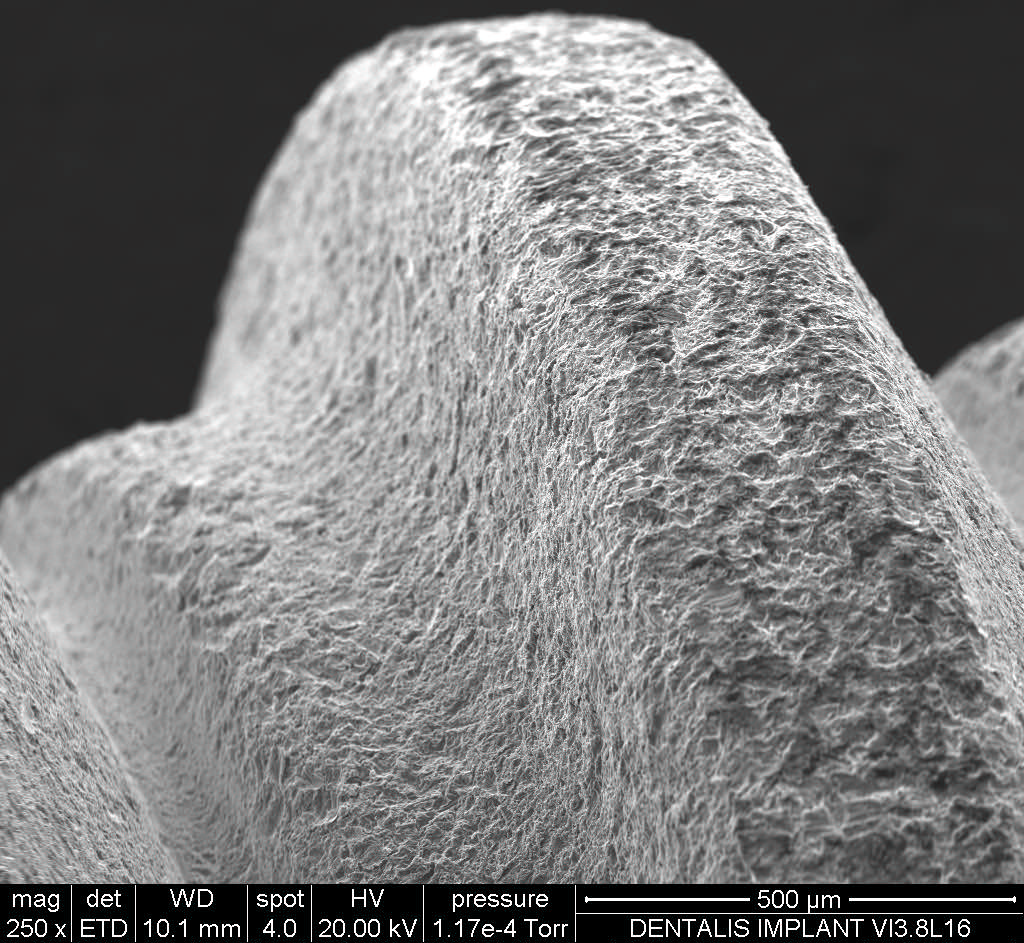

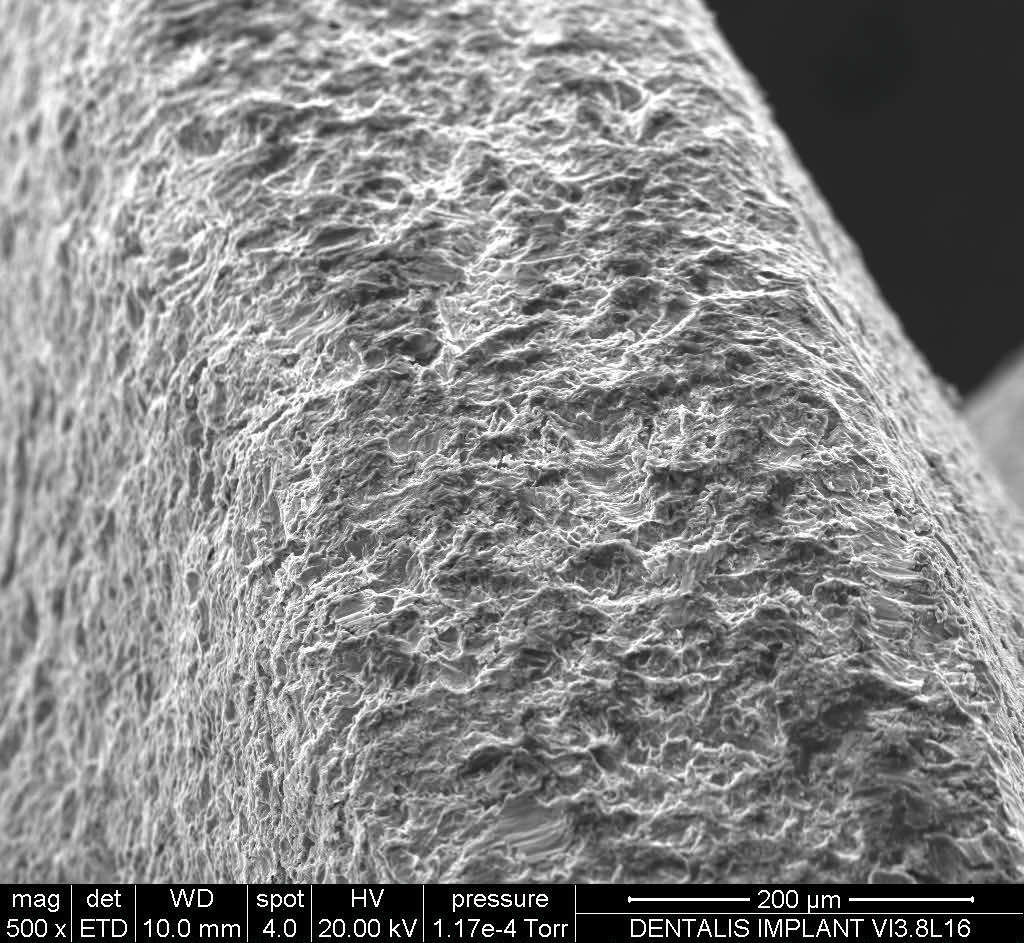
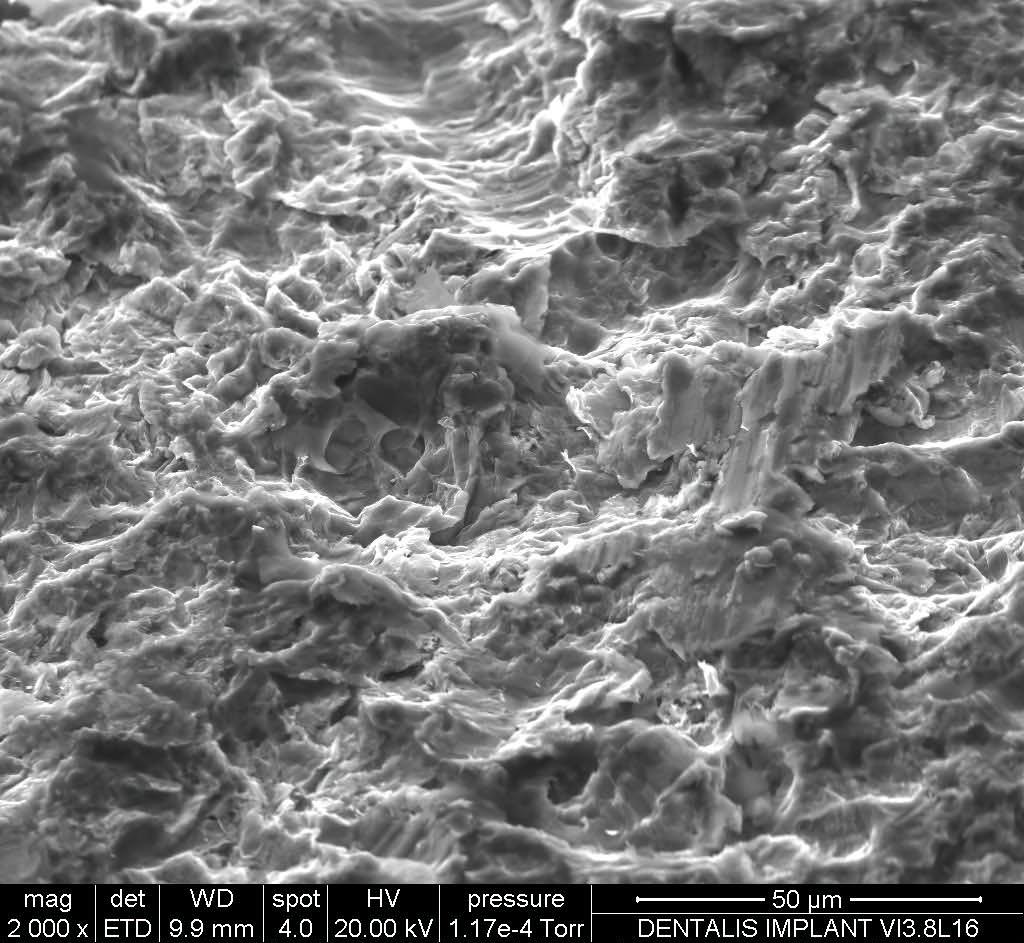
Roughness is measured with an average roughness (Ra), while the most commonly used parameter for describing roughness is calculated in microns. The rough surfaces produced by grit-blasting have irregular geometries with Ra value of 3.0 μm, which is considered optimal for the osseointegration process.
Raw Material:
All Dentalis implants are made of Ti 6Al-4V ELI that is a higher-purity (“extra-low interstitial”) version of Ti 6Al-4V, with lower specified limits on iron and the interstitial elements C and O. It is an alpha + beta alloy .Ti 6Al-4V ELI may be considered in any biomedical application, particularly for implantable components, because of its biocompatibility, good fatigue strength, and low modulus. Ti 6Al-4V ELI has been the material of choice due to its excellent biocompatibility. The ELI grade has superior damage tolerance (fracture toughness, fatigue crack growth rate) and better mechanical properties compared to standard grade Ti 6Al-4V.
Drilling procedure:
Recommendation :
To reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex. Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the depth
of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 3.25Ø in soft bone (D4)
use the 2.8 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 |

Recommendation :
To reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the depth
of the cortex For example:Implant diameter 3.75Ø in soft bone
(D4) use the 3.2 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 |

Recommendation :
To reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the
depth of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 3.75Ø
in soft bone (D4) use the 3.2 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 | 400-600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 | ∅ 4.1 |

Recommendation :
To reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the
depth of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 4.7Ø
in soft bone (D4) use the 4.1 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 | 400-600 | 300-500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 | ∅ 4.1 | ∅ 4.6 |

Recommendation :
To reduce the pressure in the bone around the implant neck:
Bone Type D1 use the last drill up to 1/3 depth.
Bone Type D2-3 use the last drill to the depth of the cortex.
Bone Type D4 use the one before last drill desirable to the
depth of the cortex For example: Implant diameter 5.0Ø in
soft bone (D4) use the 4.6 Ø drill as a final drill just for the cortex.
Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
| Drill Speed (RPM) | 900-1200 | 900-1200 | 800-1000 | 500-700 | 400-700 | 400-600 | 400-600 | 300-500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Diameter (mm) | ∅ 1.8 | ∅ 2 | ∅ 2.5 | ∅ 2.8 | ∅ 3.2 | ∅ 3.6 | ∅ 4.1 | ∅ 4.6 |

Procedures recommended by DENTALIS cannot replace the judgment and professional experience of the surgeon.
The combination of innovative surface technology with 344% stronger bone reduces marginal bone loss and provides for a higher BIC%, decreasing
the risk of peri-implant disease. The enhanced deep thread simplifies the insertion and allows for high primary stability.
This is the first dental implant to combine the concept of tissue-level
implants with an anti-bacterial coating on the implant neck, preventing
peri-implant disease and providing predictable results you can trust.
The combination of innovative surface technology with 344% stronger bone reduces marginal bone loss and provides for a higher BIC%, decreasing
the risk of peri-implant disease. The enhanced deep thread simplifies the insertion and allows for high primary stability.
This is the first dental implant to combine the concept of tissue-level implants with an anti-bacterial coating on the implant neck,
preventing peri-implant disease and
providing predictable results
you can trust.
The combination of innovative surface technology with 344% stronger bone reduces marginal bone loss and provides for a higher BIC%, decreasing
the risk of peri-implant disease. The enhanced deep thread simplifies the insertion and allows for high primary stability.
This is the first dental implant to combine the concept of tissue-level implants with an anti-bacterial coating on the implant neck,
preventing peri-implant disease and
providing predictable results
you can trust.

Stay Safe. Wear a Mask!
The pink tissue versatile implant neck combines superior gingival aesthetics and high primary stability, improved placement,
and temporization, which is particularly beneficial in
aesthetically demanding cases.
REFERENCES:
1.Bittner N, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Gil M. Comparison of Peri-implant Soft Tissue Color with the Use of Pink-Neck vs Gray Implants and Abutments Based on Soft Tissue Thickness:
A 6-Month Follow-up Study. Int J Prosthodont. 2020Jan/Feb;33(1):29-38.
2. Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Bittner N. Comparison of the Color Appearance of Peri-implant Soft Tissue with Natural Gingiva Using Anodized Pink-Neck Implants and Pink Abutments: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019 May/June;34(3):752–758.
3.Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H. A prospective clinical trial to assess the optical efficacy of pink neck implants and pink abutments on soft tissue aesthetics. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017;29(6):1-7.38.
The pink tissue versatile implant neck combines superior gingival aesthetics and high primary stability, improved placement, and temporization, which is particularly beneficial in aesthetically demanding cases.

REFERENCES:
1.Bittner N, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Gil M. Comparison of Peri-implant Soft Tissue Color with the Use of Pink-Neck vs Gray Implants and Abutments Based on Soft Tissue Thickness:
A 6-Month Follow-up Study. Int J Prosthodont. 2020Jan/Feb;33(1):29-38.
2. Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H, Da Silva J, Kim D, Tarnow D, Schulze-Späte U, Cleber S, Bittner N. Comparison of the Color Appearance of Peri-implant Soft Tissue with Natural Gingiva Using Anodized Pink-Neck Implants and Pink Abutments: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019 May/June;34(3):752–758.
3.Gil M, Ishikawa-Nagai S, Elani H. A prospective clinical trial to assess the optical efficacy of pink neck implants and pink abutments on soft tissue aesthetics. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017;29(6):1-7.38.
